Graphite structure and properties
Structure
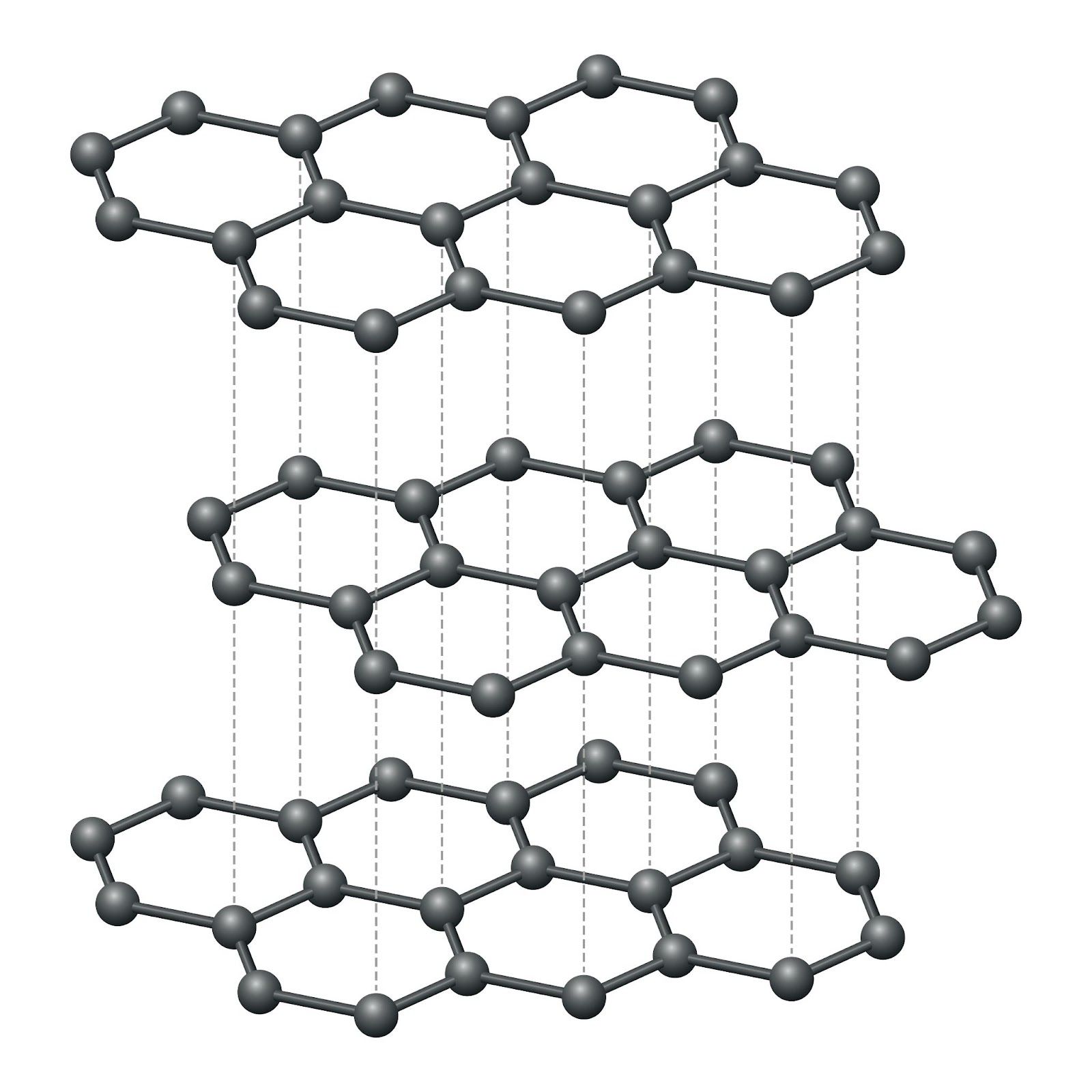
- Graphite takes the form of a stack of carbon atom planes, or “graphene planes”.
- There are strong covalent bonds within a plane and weak bonds between planes.
Properties
- Graphite is a lightweight material, with high thermal and electrical conductivity and resistance to heat and friction
- It is inert, non-toxic and recyclable.
Biographite
Biographite is produced from forestry waste:
- Protect the environment compared to the use of petroleum coke or mined materials.
- Better technical and economic recovery of waste.
- Develop a sustainable, circular and sovereign solution.
A responsible and sustainable solution
- Sourcing of raw materials within a local perimeter of less than 70km
- Biomass is thermally treated at lower temperatures, using inductive heating (green energy), which generates heat directly within the solid without unnecessarily heating the whole device, as is the case with the indirect convection and conduction heaters currently in use (2500° to 3000°).
- the treatment time is 3 days, a 10-fold reduction compared to current heating processes,
Applicatives
Anode Battery
Graphite makes up 95% of the composition of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, making it crucial to the global transition to electric vehicles.
Thermal resistance
Refractory materials, essential for high-temperature equipment such as furnaces and nozzles, feature graphite protection.
Surface treatment
Graphite surface treatment helps reduce friction and resist corrosion in marine environments, for example, as well as ensuring resistance to aggressive environments and equipment subjected to chemically altered conditions.